Overview
Section 847 of the FY20 National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) requires the Department of War (DOW) to improve its risk assessment and mitigation of foreign ownership, control, or influence (FOCI) of its contractors and subcontractors. NDAA, Section 847 includes assessing whether contractors and subcontractors disclose their beneficial ownership and if they are under any Foreign Ownership, Control or Influence (FOCI) to the Defense Counterintelligence and Security Agency. Beneficial ownership identifies the true individuals or entities who ultimately own or control a business, even if through indirect means, to assess potential foreign influence. This transparency helps the DOW mitigate security risks and ensure foreign entities cannot compromise sensitive defense operations or classified information.
NDAA, Section 847 also requires covered contractors and subcontractors to periodically have their compliance with the FOCI disclosure requirements assessed and to re-assess contractors and subcontractors when a changed condition is submitted. This applies to any DOW contractor or subcontractor that has a contract worth $5 million.
This requirement is an expansion of existing FOCI vetting requirements to pre-award contract activities and unclassified contracts. DCSA is currently preparing and setting the foundation for the publications of the Defense Federal Acquisition Regulation Supplement (DFARS) clause and execution of this mission, which is anticipated in the next 12-18 months. DFARS is a set of regulations that supplements the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) and provides specific guidance and rules for the Department of War (DOW) acquisition process. It governs the procurement of goods and services for defense purposes and ensures that these processes align with national security requirements, defense policies, and statutory obligations.
The DFARS is important because it tailors acquisition rules to the unique needs of the Department of War, ensures regulatory compliance, streamlines procurement processes, manages risks, and aligns defense acquisitions with legislative mandates.
DCSA will execute the NDAA requirements to protect our critical technologies and information. DCSA and Military Departments will be taking a collective whole of government effort to resist and deter adversaries vying for advantages in this effort. Joint efforts such as this are crucial to ensuring a continued economic and military advantage.
As the DOW engages to enact the Secretary of War's priority of revitalizing the defense industrial base (DIB), DCSA will act to ensure the protection of our national security through actions such as NDAA, Section 847. This process represents acquisition reform within the country; a factor to not only revitalizing the DIB but also to encourage new companies to join the growing defense ecosystem.
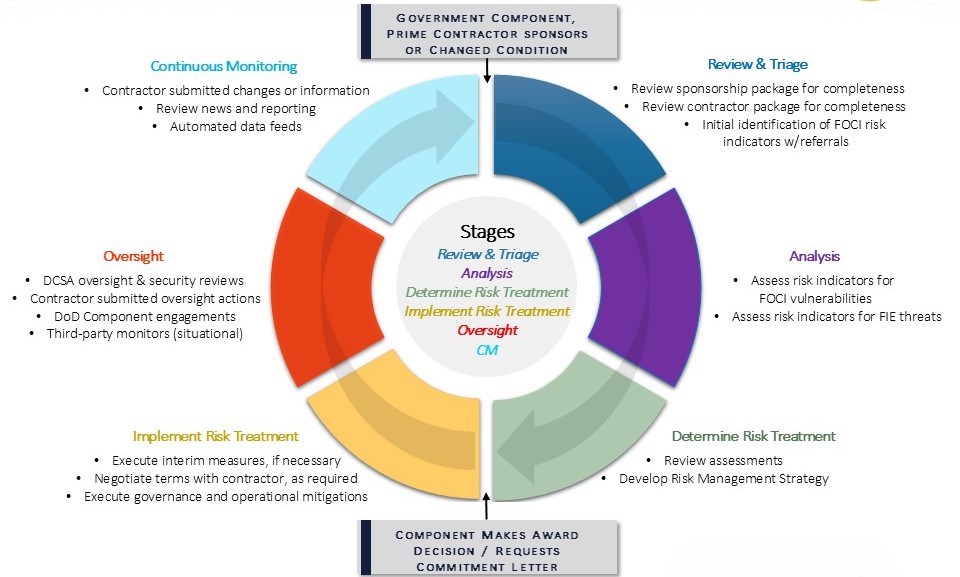
NDAA, Section 847 one-pager
DCSA Role in NDAA, Section 847
DCSA is the primary DOW agency tasked with reviewing and adjudicating all contractors that meet these criteria of NDAA, Section 847 of the FY20 National Defense Authorization Act. DCSA will provide a complete case review for all contractors covered under this requirement, initially and when changes occur. DCSA will provide case review and compliance information, prior to contract award, to our DOW partners at scale, quality, and within timelines.
DCSA has the necessary resources to conduct the mission, set forth the implementation plans and hiring actions to meet this new requirement, and stands ready to execute as soon as the DFARS clause is completed.
Security Impact
NDAA, Section 847 of the NDAA serves as a vital tool in minimizing national security risks associated with foreign influence in the defense sector. It impacts the acquisition community by mandating thorough vetting of contractors, affects the defense industrial base by requiring proactive measures against FOCI, and involves the DCSA in overseeing compliance.
By collectively focusing on reducing these risks, NDAA, Section 847 helps protect sensitive technologies and classified information, thereby reinforcing the security and resilience of the United States. NDAA, Section 847 seeks to prevent unauthorized foreign access to classified information and safeguard the integrity of the nation's defense capabilities.
Under NDAA, Section 847 many communities and organizations will be affected. Within the acquisition community this will lead to a fundamental change to pre-award due diligence and increased engagement and collaboration with security communities.
For the Defense Industrial Base (DIB), this will mean a tougher look and additional scrutiny for unclassified contracts and support to the DOW, in the pursuit of national security. DCSA will have a large role as well, providing direct support to the pre-award acquisition lifecycle. This will result in significant increase in the volume of FOCI reviews to support the NDAA, Section 847 program.
FOCI/Beneficial Ownership Pre-Award Lifecycle