What is Continuous Vetting?
Continuous Vetting (CV) is a process that involves regularly reviewing a cleared individual’s background to ensure they continue to meet security clearance requirements and should continue to hold positions of trust.
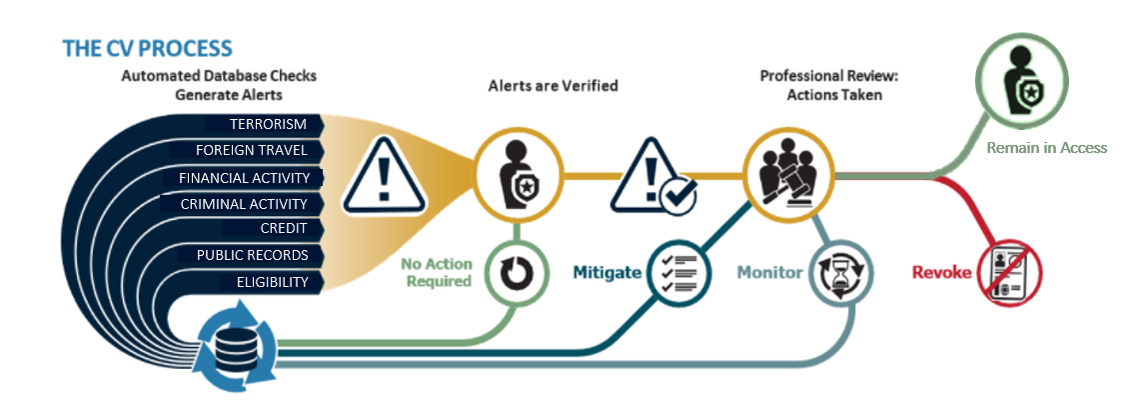
How does the Continuous Vetting (CV) process work?
Automated record checks pull data from criminal, terrorism, and financial databases, as well as public records, at any time during an individual’s period of eligibility. When DCSA receives an alert, it assesses whether the alert is valid and worthy of further investigation. DCSA investigators and adjudicators then gather facts and make clearance determinations. CV helps DCSA mitigate personnel security situations before they become larger problems, either by working with the cleared individual to mitigate potential issues, or in some cases suspending or revoking clearances.
Trusted Workforce 2.0
Trusted Workforce 2.0, the whole-of-government approach to reform the personnel security process and establish a single vetting system for the U.S. Government, began implementation in 2018 following extensive planning and interagency coordination.
The National Background Investigation Services (NBIS) is the backbone of TW 2.0, serving as the secure IT system that will coordinate and connect the systems, interfaces and databases that support continuous vetting.
How NBIS Supports
National Background Investigation Services (NBIS) is the new personnel vetting IT system that is transforming the background investigation process to deliver stronger security, faster processing, and better information sharing, it will replace a suite of outdated, legacy IT systems that no longer meet the needs of the U.S. government. It is the future of personnel vetting, enabling the federal government to fully meet necessary TW 2.0 policy reforms.
DCSA is planning
NBIS capability deployment and onboarding/adoption in a phased approach. This gradual rollout is designed to ensure NBIS capabilities have gone through significant user acceptance testing.